How to Set Up BigQuery with ContextFlo: A Complete Guide
Learn how to connect Google BigQuery to ContextFlo. This step-by-step guide covers creating a service account with proper permissions, downloading credentials, and uploading them to ContextFlo.
Google BigQuery is a serverless, highly scalable cloud data warehouse that makes it easy to analyze massive datasets. Setting up BigQuery with ContextFlo allows you to query your data, create metrics, and build powerful analytics dashboards.
This guide walks you through the complete process: creating a service account with the right permissions, downloading your credentials, and uploading them to ContextFlo.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have:
- ✓Admin access to a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) project
- ✓BigQuery API enabled in your project
- ✓Permission to create service accounts and assign IAM roles
Step 1: Create a Service Account
A service account is a special type of Google account that represents an application rather than a person. ContextFlo will use this service account to securely access your BigQuery data.
Navigate to IAM & Admin
In the Google Cloud Console, open the navigation menu and select IAM & Admin → Service Accounts.
💡 Tip: You can also search for "Service Accounts" in the top search bar.
Create New Service Account
Click + CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT at the top of the page.
Fill in the details:
- • Service account name:
contextflo-bigquery - • Service account ID: Auto-generated (e.g.,
[email protected]) - • Description:
Service account for ContextFlo to read BigQuery data
Grant BigQuery Permissions
Click Continue to assign roles to your service account.
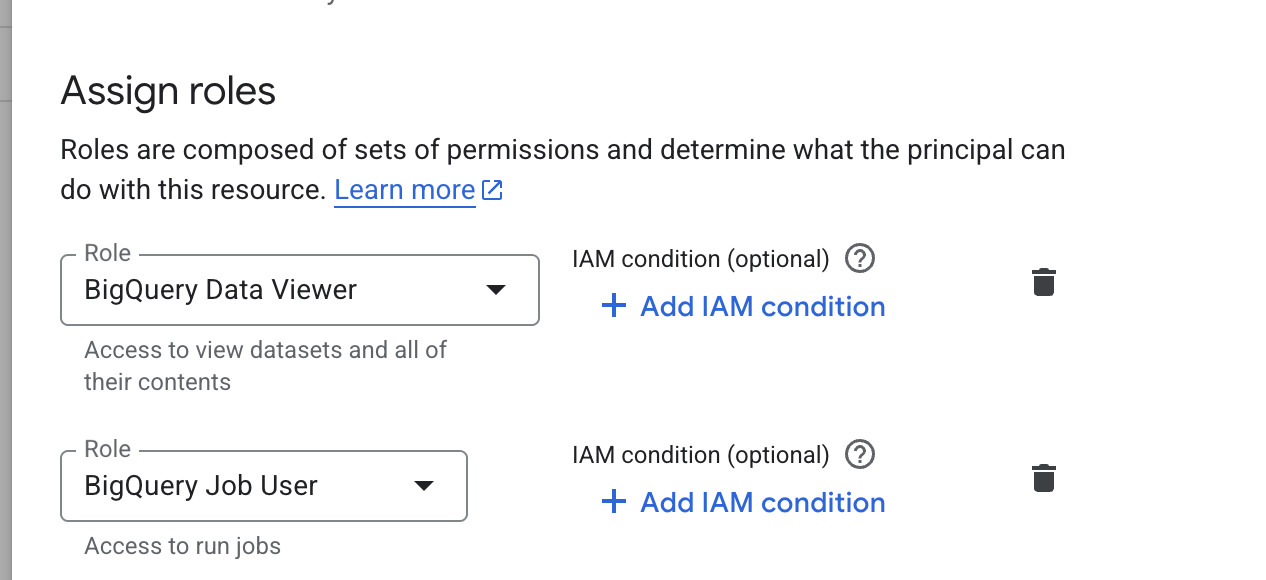
Required IAM Roles
Add the following roles to grant ContextFlo read-only access to your BigQuery data:
- •
BigQuery Data Viewer— Read access to BigQuery tables and datasets - •
BigQuery Job User— Permission to run queries
⚠️ Security Best Practice: These roles provide read-only access, ensuring ContextFlo cannot modify or delete your data.
Complete Creation
Click Continue and then Done to create the service account. You can skip the optional "Grant users access" step.
Step 2: Download Service Account Credentials
After creating the service account, you need to generate and download a JSON key file. This file contains the credentials ContextFlo will use to authenticate with BigQuery.
Locate Your Service Account
In the Service Accounts list, find the contextflo-bigquery service account you just created.
Manage Keys
Click on the three dots (⋮) menu on the right side of the service account row, then select Manage keys.
Create New Key
Click ADD KEY → Create new key.
Select JSON as the key type (this is the default and recommended format).
Download JSON File
Click CREATE. The JSON key file will automatically download to your computer.
🔒 Security Warning: This JSON file contains sensitive credentials. Store it securely and never commit it to version control (add it to your .gitignore file).
The downloaded file will have a name like: project-name-abc123-1234567890ab.json
📄 What's Inside the JSON Key File?
The JSON file contains authentication credentials. Here's what it looks like (with sensitive data redacted):
{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "your-project-id",
"private_key_id": "abc123...",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n...\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "[email protected]",
"client_id": "123456789...",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/..."
}Step 3: Upload Credentials to ContextFlo
Now that you have your service account credentials, you're ready to connect BigQuery to ContextFlo.
Navigate to Data Sources
In ContextFlo, go to your organization settings and click on Data Sources.
Add BigQuery Connection
Click + Add Data Source and select BigQuery from the list of available databases.
Fill in Connection Details
Connection Form Fields
- Connection Name: A friendly name for this connection (e.g., "Production Analytics")
- Description: Optional notes about this connection
- Project ID: Your GCP project ID (found in the JSON file as
project_id) - Location: The region where your BigQuery datasets are located (e.g., "US", "EU", "us-central1")
- Service Account JSON: Upload or paste your JSON key file
Upload the JSON Key
You have two options:
Option A: Upload File
Click Choose File and select the JSON file you downloaded from Google Cloud.
Option B: Paste JSON
Open the JSON file in a text editor, copy the entire contents, and paste it into the text area.
Test the Connection
Before saving, click Test Connection to verify that ContextFlo can successfully connect to your BigQuery project.
✅ Success: If the test passes, you'll see a confirmation message. This means your credentials are valid and permissions are correctly configured.
❌ Failed: If the test fails, double-check your Project ID, location, and ensure the service account has the required IAM roles.
Save and Start Querying
Click Connect to save your BigQuery connection. You're now ready to query your data, create metrics, and build dashboards!
Troubleshooting Common Issues
🔍 "Permission Denied" Error
Cause: The service account doesn't have the required IAM roles.
Solution: Return to the IAM & Admin section in Google Cloud Console and verify that all three required roles are assigned to your service account.
🔍 "Invalid JSON" Error
Cause: The JSON file format is corrupted or incomplete.
Solution: Re-download the JSON key file from Google Cloud Console. Make sure you copied the entire file contents if pasting manually.
🔍 "Project Not Found" Error
Cause: The Project ID is incorrect or the BigQuery API is not enabled.
Solution: Double-check your Project ID in the Google Cloud Console. Also ensure the BigQuery API is enabled in your project (APIs & Services → Library → BigQuery API → Enable).
🔍 "Location Mismatch" Error
Cause: The location specified doesn't match where your datasets are stored.
Solution: Check your BigQuery dataset locations in the Google Cloud Console and use the matching region code. Common locations: "US" (multi-region), "EU" (multi-region), "us-central1", "europe-west1".
Security Best Practices
- 🔐Use read-only permissions: The IAM roles recommended in this guide provide read-only access, ensuring ContextFlo cannot modify or delete your data.
- 🔑Rotate keys regularly: Consider rotating service account keys periodically (e.g., every 90 days) as a security best practice.
- 📁Never commit credentials: Add JSON key files to your
.gitignoreto prevent accidental commits to version control. - 👥Limit dataset access: If you only need access to specific datasets, you can grant dataset-level permissions instead of project-level permissions for tighter security.
- 📊Monitor usage: Use Google Cloud's audit logs to monitor service account activity and ensure it's being used as expected.
What's Next?
Congratulations! You've successfully connected BigQuery to ContextFlo. Here's what you can do next:
📊 Create Metrics
Start defining metrics from your BigQuery tables. Write SQL queries to calculate KPIs and track business performance.
🌳 Build Metric Trees
Organize your metrics into hierarchical trees to understand how different metrics relate to your north-star KPIs.
💬 Ask Questions
Use ContextFlo's AI assistant to ask questions about your data in natural language and get instant insights.
📈 Create Dashboards
Build interactive dashboards to visualize your metrics and share insights with your team.
Need Help?
If you're experiencing issues or have questions about setting up BigQuery with ContextFlo, we're here to help:
- 📧 Email: [email protected]
- 📚 Documentation: View our data source connection guides